What is the Difference between Collagen? Collagen peptides are broken-down fragments that are easier to absorb, while collagen is a structural protein that provides support and elasticity to tissues, skin, and bones.
Collagen peptides, on the other hand, are hydrolyzed collagen molecules broken down into smaller peptides for easier digestion and absorption in the body. This difference in structure affects their bioavailability and how they benefit overall health. Collagen supplements, particularly peptides, have gained popularity for promoting skin health, joint function, and muscle strength.
Understanding the variance between collagen and collagen peptides can help individuals make informed choices when selecting the right supplement to support their wellness goals.
Credit: cbsupplements.com
Composition
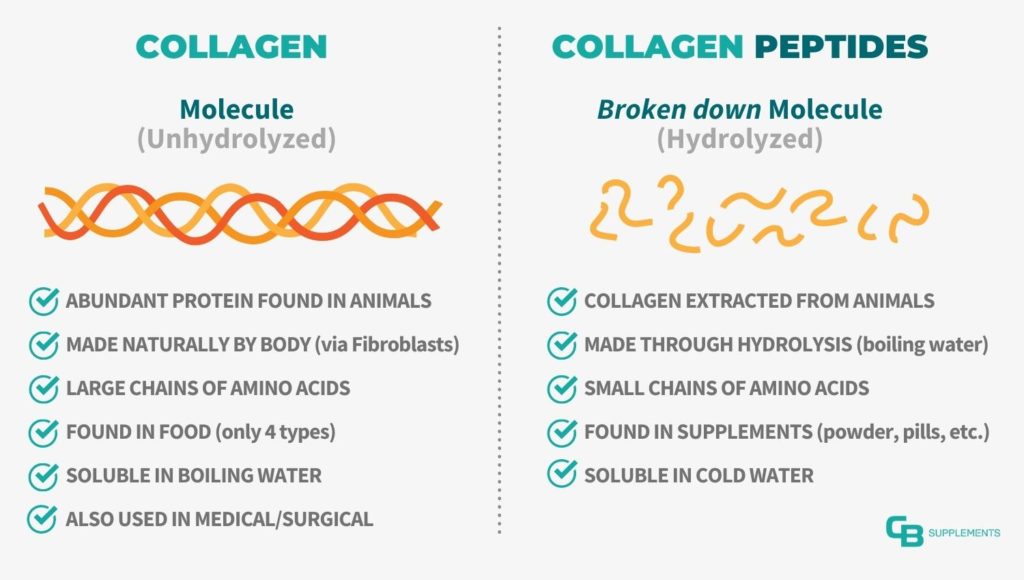
Collagen is the most abundant protein in the human body, constituting a significant portion of the connective tissues, such as skin, ligaments, and tendons. It is a complex structure primarily made of three long chains of amino acids wound together to form a triple helix. In contrast, collagen peptides are the result of the hydrolysis process, breaking down the long chains of collagen into smaller peptides, which are more easily absorbed and utilized by the body.
Defining Collagen
Collagen is a fibrous protein that provides strength and structure to the body, similar to the function of scaffolding supporting a building. It is made up of three long polypeptide chains, rich in amino acids like glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline, which form a unique triple helical structure.
Explaining Collagen Peptides
Collagen peptides, also known as hydrolyzed collagen, are formed by breaking down the collagen protein into smaller peptide chains. This results in a form of collagen that is easily digestible and soluble in water, making it highly bioavailable for the body. Enzymatic hydrolysis helps fragment the collagen, leading to the formation of peptides, often referred to as collagen peptides.
Credit: www.pinterest.com
Sources
Collagen peptides are the broken-down versions of collagen, making them more accessible for the body to digest and absorb. They are usually considered the best form of collagen for ingestion and are commonly used as a collagen supplement. On the other hand, collagen refers to the complete protein itself, which can be difficult for the body to digest and absorb.
Animal Vs. Plant Sources
Collagen is derived from animal connective tissues, such as bones and skin, while collagen peptides are hydrolyzed forms of collagen.
Collagen peptides are more digestible than whole collagen due to their smaller peptide size.
Animal Sources
- Primary sources are beef, fish, and chicken.
- Contains essential amino acids like proline and glycine.
- Supports skin, bone, and muscle health.
Plant Sources
- Include plant-based proteins like soy, beans, and nuts.
- It may lack specific amino acids found in animal collagen.
- Suitable for vegetarians and vegans.
Processing
One key difference between collagen and collagen peptides is the processing methods used to extract and produce these supplements. Understanding these techniques can help you choose the right form of collagen for your needs.
Traditional Collagen Extraction
In traditional collagen extraction, the collagen is sourced from animal connective tissues, such as bones and skin. The process involves boiling these tissues in water for an extended period to release the collagen proteins. Once the collagen is extracted, it is typically dried and ground into a fine powder for use in supplements.
This method of extraction retains the complete structure of the collagen protein, including its more considerable molecular weight. While traditional collagen provides the full spectrum of collagen types, its larger size may make it less easily digested and absorbed by the body.
Hydrolysis For Collagen Peptides
On the other hand, collagen peptides undergo a process called hydrolysis. This process involves breaking down the larger collagen proteins into smaller peptide fragments through the use of enzymes or heat. The resulting collagen peptides have a lower molecular weight and are more accessible for the body to digest and absorb.
Hydrolyzed collagen peptides are typically produced using enzymatic hydrolysis or enzymatic treatment, which breaks the long collagen protein chains into smaller peptides. These peptides are then filtered and dried to create a fine powder that can be easily dissolved in both hot and cold liquids.
Since collagen peptides have a lower molecular weight, they are often recommended for individuals looking for better absorption and utilization of collagen in the body. Their smaller size allows them to be broken down more quickly during digestion, making the amino acids more readily available for the production of collagen within the body.
In conclusion, the processing methods used for collagen and collagen peptides result in different forms of the protein. Traditional collagen extraction retains the complete structure of the protein but may be less easily digested, while collagen peptides undergo hydrolysis to create smaller and more easily absorbed peptides. Consider your specific needs and preferences when choosing between these two forms of collagen.
Credit: www.absolutecollagen.com
Bioavailability
Bioavailability is an important aspect to consider when comparing collagen and collagen peptides. It refers to the body’s ability to absorb and utilize a substance, and in the case of these supplements, it directly impacts their effectiveness. Understanding the difference in bioavailability between collagen and collagen peptides can help individuals make informed decisions about which form is best suited for their needs.
Difference In Absorption:
When it comes to bioavailability, collagen and collagen peptides exhibit notable differences in absorption within the body. Collagen, in its original form, often found in bone broth or animal tissues, has a large molecular structure, making it challenging for the body to break down and absorb efficiently. On the other hand, collagen peptides are hydrolyzed, meaning they have been broken down into smaller, bioactive peptides. As a result, collagen peptides demonstrate higher bioavailability compared to regular collagen, allowing for easier absorption and utilization within the body.
Health Benefits
Collagen and collagen peptides offer various health benefits, each impacting different areas of the body.
Impact On Skin & Hair
Collagen:
- Supports skin elasticity and hydration.
- It may reduce wrinkles and improve skin texture.
- Strengthens hair follicles for healthier hair.
Collagen Peptides:
- Enhance skin firmness and elasticity.
- Boost hair growth and thickness.
- Provide essential amino acids for skin and hair health.
Effect On Bone & Joint Health
Collagen:
- Supports bone density and strength.
- Provides structural support for joints.
- It may help reduce joint pain and inflammation.
Collagen Peptides:
- Promote bone formation and mineralization.
- Improve joint flexibility and mobility.
- Support overall joint health and reduce the risk of fractures.
Supplementation
When it comes to supplementation, understanding the difference between collagen and collagen peptides is crucial in determining their unique benefits for overall health. Collagen, the most abundant protein in our bodies, provides structure to skin, bones, muscles, and tendons. On the other hand, collagen peptides, also known as hydrolyzed collagen, are broken down into smaller peptides, making them easily digestible and absorbable by the body. This subtle difference influences the form, consumption, and individual benefits of both collagen and collagen peptides.
Choosing The Right Form
When selecting the correct form of supplementation, it is essential to consider the specific needs and goals. Collagen comes in various types, such as type I, II, and III, each catering to particular areas like skin, joint, or muscle health. On the contrary, collagen peptides are more versatile and easily absorbed, making them a preferred choice for overall well-being.
Considerations For Consumption
Consumption considerations play a significant role in the efficacy of collagen and collagen peptides. While collagen can be consumed in multiple ways, such as through bone broth or whole food sources, collagen peptides offer the advantage of being convenient to add to beverages or recipes due to their easy dissolvability.
What is the Difference between Collagen? Frequently Asked Questions
Which Is Better, Collagen Or Collagen Peptides?
Collagen peptides are considered the best form of collagen. They are broken down into small peptides, making them more accessible for the body to digest. Collagen supplements, on the other hand, are not as easily absorbed. Collagen peptides also have fewer side effects, such as mild digestive symptoms.
In conclusion, collagen peptides are better for ingestion.
Which Form Of Collagen Is Most Effective?
Collagen peptides are the most effective form of collagen for ingestion since they are easy to digest.
Is There A Downside To Taking Collagen Peptides?
Collagen peptides are generally safe, with few side effects, like mild digestive symptoms. They are easily digested and beneficial for skin, bone, and muscle health.
Is Collagen Builder The Same As Collagen Peptides?
Collagen builders and collagen peptides are not the same. Collagen peptides are broken-down versions of complete collagen, supporting skin, bone, and muscle health. In contrast, collagen builders focus on producing complete collagen in the body.
Conclusion
Collagen and collagen peptides both offer unique benefits. Collagen peptides are the preferred option for ingestion due to their easy digestibility. With hydrolyzed collagen, the body can efficiently absorb the peptides, enhancing overall health. Consider collagen peptides for a convenient and effective collagen supplement.